Jurisdiction under BNS

Jurisdiction derived from the Latin phrase “Juris Dicere” in which Juris means Law and Dicere means to speak. In legal context, it refers to the authority or dominion on a legal body to do justice.
Introduction
India is a sovereign nation, and like every sovereign state, it has the right to make laws and enforce them within its territory. However, with increasing global interaction, crimes are no longer confined to national boundaries. Offences can be committed by Indian citizens abroad, or by foreigners affecting Indian citizens or interests. To tackle such evolving criminal scenarios, the BNS expanded the jurisdiction. Jurisdiction refers to the legal authority or power of Indian courts to try and punish individuals for criminal offences.
Jurisdiction derived from the Latin phrase “Juris Dicere” in which Juris means Law and Dicere means to speak. In legal context, it refers to the authority or dominion on a legal body to do justice.
Types of Jurisdictions under Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita
- Intra Territorial Jurisdiction (Section 1(3) BNS)
- Extra Territorial Jurisdiction (Section 1(4) and 1(5) BNS)
- Admiralty Jurisdiction
Intra Territorial Jurisdiction
Section 1(3) of the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita deals with the Intra Territorial Jurisdiction.
- Punishment for offences committed within India (Section 1(3))
It states that Every Person (Whether citizen or non-citizen) shall be liable to punished within India under this code for every act or omission which are contrary to this sanhita.
The Words “Within India” has to be given a liberal interpretation means that it also includes persons outside india who does offence directly incidental upon the territory of India.
Examples: X and Y from Bangladesh does conspiracy to commit offence in india, X and Y both are punished under this section
Exceptions
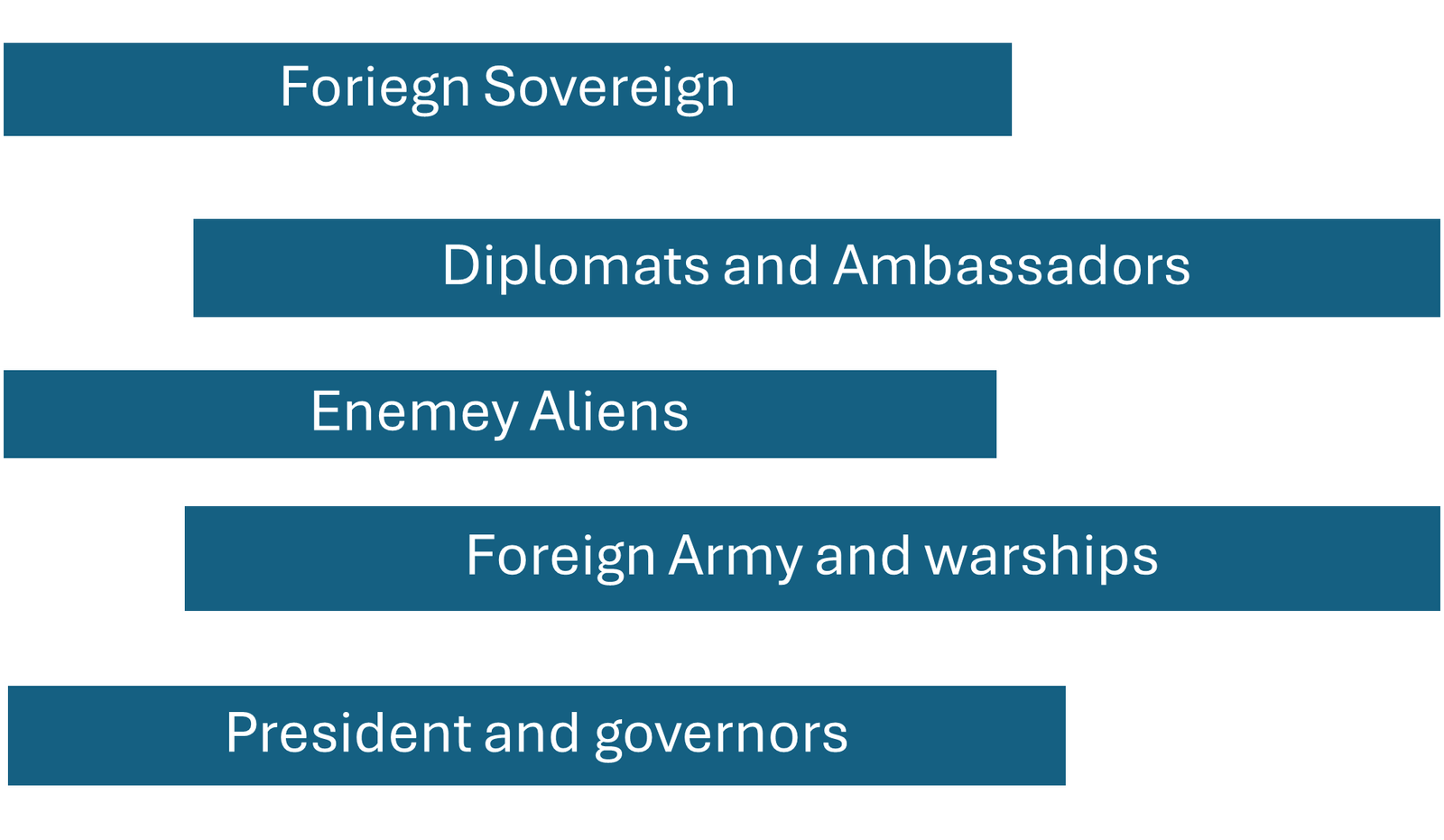
Case Laws
Case- Mobarik Ali Vs. State of Bombay AIR 1957 SC
Held- The Court held that the basis U/S 2 of Indian Penal code is not the corporeal presence of the offender but the locality where the offence is committed. It is immaterial that he is not present at the time of commission of the offence within territory of India.
Case- State of Maharashtra Vs. Mayer Hans George AIR 1965 SC
Held- The Court held that the foreigner is liable under foreign exchange regulation Act, 1973 where he without making an express declaration about the gold which he was carrying during his journey through the aeroplane. he was held liable as soon as the plane landed on the territory of India.
Extra Territorial Jurisdiction
Section 1(4) and 1(5) of the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita deals with the Extra Territorial Jurisdiction and its extension.
- Punishment for offences committed beyond India but tried within India (Section 1(4))
It states that Any person committed an offence beyond india shall be dealt under Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita in the same manner as if such act had been committed within India.
A Legal Fiction has been created under section 1(4) of BNS.
- Extension of the Code to extra territorial offences (Section 1(5))
The provisions of Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita also apply in these offences committed:
- By any Citizen of India without and beyond India
- By any person on any ship or aircraft registered in India
- By any person in any place targeting computer resource located in India.
Example: A (citizen of india) commit murder in Uganda; He can be tried and convicted of murder in any place in india in which he may be found
Admiralty Jurisdiction
- It is a jurisdiction which confers the power to try offences which are committed on high seas.
- The notion that a ship floats on the high seas is like a floating island is the basic principle behind the admiralty jurisdiction.
- The extension of admiralty jurisdiction is over the cases which involve the following offences:
- Offences which are committed on the Indian ships on the high seas
- Offences which are committed in foreign ships within Indian territorial waters
- piracy
Example: Indian ship kills Australian ship on high seas; it will be punishable under this Sanhita.
Conclusion
Jurisdiction under Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita just not confined within its own territory, but it ensures that Citizens are accountable globally for their unlawful act. Due to the growth in digital era, Offences targeting India’s cyber infrastructure are covered. It reinforces the principle that justice should not be confined by boundaries, especially in an era of global interaction and digital crimes. The legislature timely making laws on jurisdictions to deliver justice not only india but also outside india. It also reflects the power and limitations of courts to try matters before them.